2024. 1. 25. 15:09ㆍAlgorithm/자료구조
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1927
1927번: 최소 힙
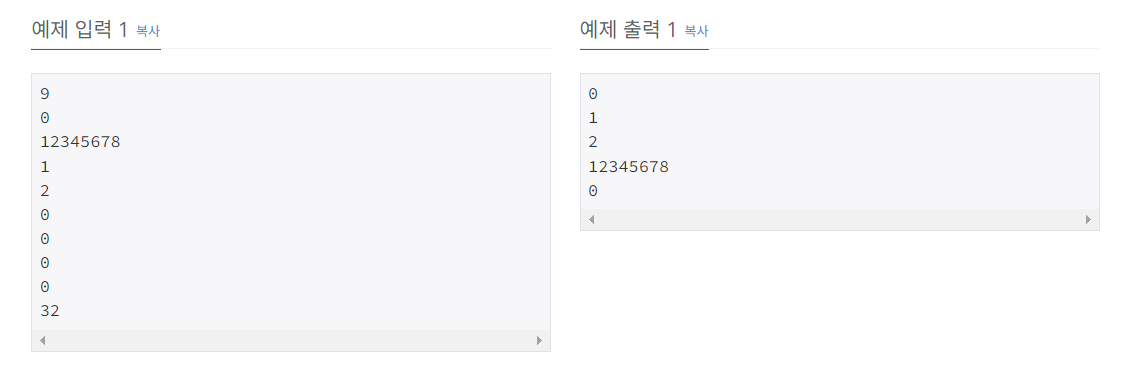
첫째 줄에 연산의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000)이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 연산에 대한 정보를 나타내는 정수 x가 주어진다. 만약 x가 자연수라면 배열에 x라는 값을 넣는(추가하는) 연산이고, x가 0
www.acmicpc.net
풀이
[1회차]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int cnt= Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
List<Integer> list= new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder sb= new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
int num= Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if(num==0) {
if(list.isEmpty()) {
sb.append("0\n");
}else {
Collections.sort(list);
sb.append(list.get(0)+"\n");
list.remove(0);
}
}else {
list.add(num);
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}결과: 시간초과
원인:
* 최악의경우
n번의 케이스 * 정렬알고리즘 시간복잡도
= n* n log(n)
= n^2 log(n)
이 때, n<=100,000
n^2= 100000 00000
= 100억
1억번의 계산을 처리하는데 걸리는시간 = 약 1초
=> 100억= 100초 (** 이 문제에서 2초밖에 주어지지 않음)
[최종]
package dataStructure;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class Ex1924 {
static List<Integer> list= new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int cnt= Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
StringBuilder sb= new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
int num= Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if(num==0) {
if(list.isEmpty()) {
sb.append("0\n");
}else {
sb.append(list.get(0)+"\n");
list.remove(0);
}
}else {
int idx= 0;
if(!list.isEmpty()) {
idx= Math.abs(Collections.binarySearch(list, num)+1);
}
list.add(idx, num);
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}=> 정렬 대신 BinarySearch 사용
BinarySearch의 시간복잡도: O(logN)
* 최악의경우
n번의 케이스 * binarySearch의 시간복잡도
= n*logN
= n logN
n<=100,000
최대 100,000번의 계산처리 -> 1초이하(**1억의 계산처리에 걸리는 시간 약 1초)
최소 힙(min-Heap)
=> 우선순위 큐를 사용해 구현하면 더 간단히 해결할 수 있다.
우선순위 큐(Priority Queue): 들어간 순서에 상관없이 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나오는 것
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
//Silver_1927.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
// Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
final BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());// 1~n
int input;
PriorityQueue<Integer> minQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
input = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if (input>0) {
minQueue.add(input);
} else {
if (!minQueue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(minQueue.poll());
}
else{
System.out.println(0);
}
}
}
br.close();
}
}
참조.
https://velog.io/@gillog/Java-Priority-Queue%EC%9A%B0%EC%84%A0-%EC%88%9C%EC%9C%84-%ED%81%90
[Java] Priority Queue(우선 순위 큐)
PriorityQueue란 우선순위 큐로써 일반적인 큐의 구조 FIFO(First In First Out)를 가지면서, 데이터가 들어온 순서대로 데이터가 나가는 것이 아닌 우선순위를 먼저 결정하고 그 우선순위가 높은 데이터
velog.io
'Algorithm > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 백준(Baekjoon) 10815. 숫자카드 (0) | 2024.01.26 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 백준(Baekjoon) 11279. 최대 힙 (0) | 2024.01.26 |
| [Java] 백준(Baekjoon) 1764. 듣보잡 (1) | 2024.01.25 |
| [Java] 백준(Baekjoon) 1158. 요세푸스 문제 (0) | 2024.01.24 |
| [Java] 백준(Baekjoon) 10845. 큐 (0) | 2024.01.24 |